本文通过源码分析的方式对RocketMQ的负载均衡做一次简单的了解。
producer对MessageQueue的负载均衡
- 通过topic获取到broker的信息。
- 得到broker上的messagequeue分布信息,再通过算法对messagequeue列表长度取模,得到queueId。
1 | // 确定queue的下标 |
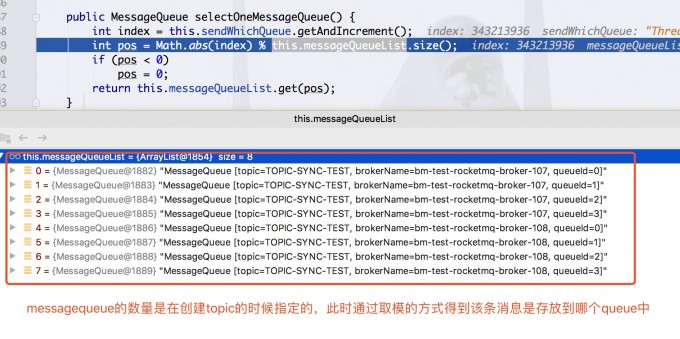
通过调试代码可以知道,所谓的MessageQueue就是broker上的队列信息,每个topic在创建的时候可以指定相应的queue的数量。也就是说,一个topic的消息存储在多个主broker中
producer负载均衡
producer端的负载均衡主要是在选择对应的broker。在producer发送消息的时候会对消息进行路由,看到底是路由到哪个broker。下面主要说下以下两种发送消息的方法:系统计算路由MessageQueue,自定义路由MessageQueue。
系统计算路由MessageQueue
1 | SendResult send = producer.send(message, 60 * 1000); |
系统计算路由MessageQueue的其他路由算法
1 | public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue(final TopicPublishInfo tpInfo, final String lastBrokerName) { |
自定义路由MessageQueue
1 | SendResult send = producer.send(message, new MessageQueueSelector() { |
Consumer的负载均衡
消费端设置负责均衡策略
在consumer.statrt()中,consumer会对所订阅的topic上的messagequeue做负载均衡DefaultConsumerPushImpl.start()下的this.rebalanceImpl.setAllocateMessageQueueStrategy(this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getAllocateMessageQueueStrategy());, 默认返回的是AllocateMessageQueueAveragely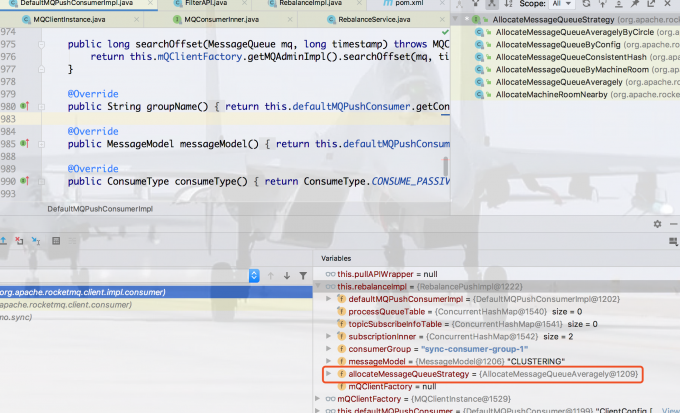
负责均衡策略
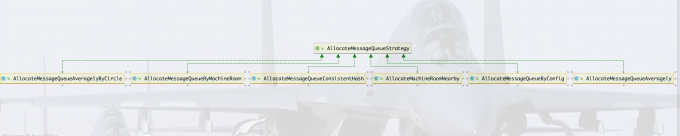
- AllocateMessageQueueAveragely
负载均衡的时机
在Consumer启动后,会通过SchedlueThreadPool来定时的计算此时此刻我这个消费者要去哪些个queue中获取消息1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13// RebalanceService
public void run() {
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
while (!this.isStopped()) {
this.waitForRunning(waitInterval);
// 开始进行分配
this.mqClientFactory.doRebalance();
}
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
具体实现1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41/**
consumerGroup : 消费组名称
currentCID:当前消费者实例Id(随机数)
mqAll: 该topic对应的queue的信息列表
cidAll: 消费组中所有的消费者列表
*/
public List<MessageQueue> allocate(String consumerGroup, String currentCID, List<MessageQueue> mqAll,
List<String> cidAll) {
if (currentCID == null || currentCID.length() < 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("currentCID is empty");
}
if (mqAll == null || mqAll.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("mqAll is null or mqAll empty");
}
if (cidAll == null || cidAll.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("cidAll is null or cidAll empty");
}
List<MessageQueue> result = new ArrayList<MessageQueue>();
if (!cidAll.contains(currentCID)) {
log.info("[BUG] ConsumerGroup: {} The consumerId: {} not in cidAll: {}",
consumerGroup,
currentCID,
cidAll);
return result;
}
int index = cidAll.indexOf(currentCID);
int mod = mqAll.size() % cidAll.size();
int averageSize =
mqAll.size() <= cidAll.size() ? 1 : (mod > 0 && index < mod ? mqAll.size() / cidAll.size()
+ 1 : mqAll.size() / cidAll.size());
int startIndex = (mod > 0 && index < mod) ? index * averageSize : index * averageSize + mod;
int range = Math.min(averageSize, mqAll.size() - startIndex);
for (int i = 0; i < range; i++) {
result.add(mqAll.get((startIndex + i) % mqAll.size()));
}
return result;
}